ClevGuard Support: Monitor Devices with Others' Permission.
Android OS imposes security restrictions to protect users. While these are sufficient for most, advanced users may want to bypass them to access more features and customization. Rooting a device allows this freedom, enabling the installation of third-party apps and system tweaks that are normally off-limits.
However, rooting comes with risks. It can expose your device to security threats, void your warranty, and stop manufacturers from providing updates. Additionally, some devices come pre-rooted, and when buying a second-hand phone, it's important to check if it's rooted.
In this article, we’ll explain how to check if your phone is rooted and why installing ClevGuard Anti-Spyware is essential for real-time protection.

Table of Contents
Part 1: What Does It Mean to Root a Phone?
Part 2: 7 Critical Signs to Tell If Your Phone Is Rooted
Part 3: Can You Unroot a Rooted Phone?
Part 4: How to Protect a Rooted Android Phone
Part 5: Conclusion
What Does It Mean to Root a Phone?
Rooting a phone refers to the process of gaining privileged access, known as "root access," to the Android operating system. This allows users to bypass the restrictions imposed by the device manufacturer or carrier and gives them the ability to modify system files, install custom ROMs, and run specialized apps that require root permissions. Rooting can unlock additional functionality, but it also comes with certain risks.
Definition of rooting a phone
Rooting a phone is essentially unlocking the Android operating system to gain full administrative rights. It’s similar to "jailbreaking" an iPhone. By rooting, users can break free from the limitations placed on the device by the manufacturer, allowing for deeper customization and control.
In a non-rooted Android phone, you are limited to performing tasks with standard user permissions. With root access, you become the "superuser," meaning you have the authority to modify the system’s core components and access areas of the operating system that are normally off-limits. This can enable advanced functions such as overclocking the processor, uninstalling pre-installed system apps (bloatware), and more.
However, rooting is not officially supported by most manufacturers, and doing so can void your warranty or cause irreversible damage to your device if not done correctly.
Is it safe to root a phone? (Pros and cons)
Rooting a device may seem to be advantageous. However, there are distinct disadvantages for which we do not recommend any user to root their device.
Pros of rooting a phone
Complete control over your device: Rooting gives you total control over your phone’s software. You can customize your phone’s appearance and functionality at a deeper level than non-rooted devices allow.
Remove bloatware: Rooting allows you to uninstall pre-installed apps that can’t be removed on non-rooted devices, freeing up storage and potentially improving performance.
Install custom ROMs: Custom ROMs are alternative versions of the Android operating system that can offer better performance, more frequent updates, and additional features that may not be available on the standard software.
Improved performance and battery life: By removing unnecessary apps and tweaking system settings, rooted phones can often achieve better performance and improved battery life.
Backup and restore: Root access allows for more comprehensive backup solutions, enabling you to backup all your data, apps, and settings in ways that aren’t possible on stock devices.
Cons of rooting a phone
Void warranty: Rooting your phone often voids the manufacturer’s warranty. If something goes wrong, you may not be able to seek help from the manufacturer.
Security risks: Rooting can make your phone more vulnerable to malware and other security threats.
Bricking your phone: If you're not careful, rooting can potentially "brick" your phone, making it unusable.
No more automatic updates: After rooting, you may lose access to official over-the-air (OTA) updates from your device’s manufacturer, requiring manual installation of software updates.
Incompatibility with certain apps: Many apps, especially banking and financial apps, will not work on rooted devices due to security concerns. Some apps may even detect root access and refuse to launch.
What happens after you root your phone?
If your phone is rooted, it opens up a world of possibilities but also brings with it a set of responsibilities. Here’s what you can expect:
Increased customization: Rooting allows you to install custom ROMs, themes, and apps, giving you more control over your device's appearance and functionality.
More control over apps:: You’ll have the ability to grant or deny specific permissions to apps, uninstall system apps, and even run apps that require root access for advanced functions.
Potential security vulnerabilities: Rooting removes many of the built-in security measures of Android. Without these protections, your device may become more vulnerable to malware, data theft, or unauthorized access by malicious apps.
Manual updates and maintenance: Since you may lose access to automatic system updates, keeping your device secure and up-to-date will often require manually installing updates or flashing custom ROMs.
Possibility of performance issues: While rooting can improve performance, improper modifications can also cause instability, app crashes, or even hardware failures.
In short, rooting provides enhanced control and flexibility but comes with significant risks that need to be carefully considered before proceeding.
7 Critical Signs to Tell If Your Phone Is Rooted
Rooting your phone can unlock advanced features, but it also opens up your device to potential security risks. If you suspect that your phone has been rooted, either by someone else or without your knowledge, here are seven critical signs to look out for:
Review your phone’s status in Settings
"Phone status official" typically indicates that your phone's operating system is the original, unmodified version provided by the manufacturer. This means it hasn't been rooted or jailbroken. This is possibly the easiest way to check if a phone is rooted or not, especially without an app.
Step 1: Go to the "Settings" app.
Step 2: Tap on the "About Phone" option.
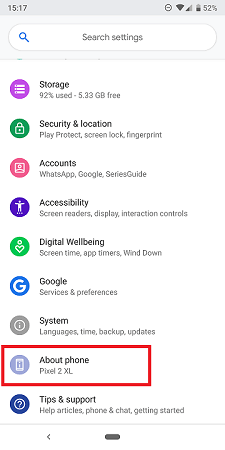
Step 3: Tap on the "Status Information" option.
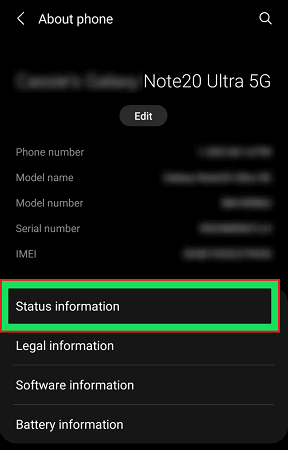
Step 4: Check the option named “Phone Status”.

If it is showing “Official”, this means your phone is NOT rooted yet. If it is showing “Custom”, this means your phone is rooted.
This is the simplest way on how to check if phone is rooted without an app. However, there are some smartphones that come rooted directly from the manufacturer. In that case, Official device status may not mean unrooted device. Therefore, for further confirmation, the following signs can help you determine whether your device is rooted.
Check for superuser or root apps
One of the clearest indicators of a rooted phone is the presence of superuser management apps like SuperSU, Magisk, or KingRoot. These apps are used to grant and manage root permissions. If you see any of these on your phone and didn’t install them, your device may be rooted.

If you find unfamiliar apps or system modifications on your phone, it's a strong indicator that your device might be rooted. Look for apps like Titanium Backup, Xposed Framework, or Root Explorer, which often require root access. If you notice these or other unusual changes that you didn't make, your phone may have been rooted.
Check root checker apps
Root Checker is an app that helps in determining if your phone is rooted or not. There are many free and paid root checker apps available on Google Play Store. Here, we have considered free Root Checker app by JoeyKrim.
Step 1: Go to Play Store.
Step 2: On the search bar, type “root checker” and tap on search icon.
Step 3: Once you see the search result, tap on Root Checker by JoeyKrim.
Step 4: Install the app and after installation, open the app.
Step 5: Once the app opens, hit the "Get Starter" button.
Step 6: Tap on the "Verify Root" option after the app identifies the model of your phone.
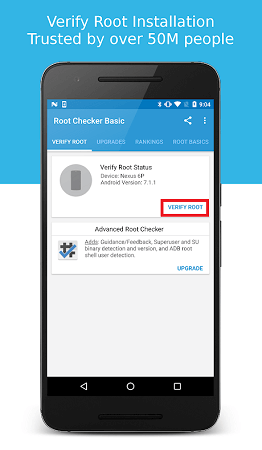
The app may take a few moments to check your device and will display a message indicating whether your phone is rooted or not.
Check by Terminal Emulator
Terminal Emulator is an app that brings Linux terminal emulator to Android devices. The app is quite useful for advanced users who have rooted their devices and want to use commands to execute various actions. At the same time, the app helps in determining whether the device is rooted or not.
Step 1: Go to your Play Store on Android.
Step 2: On the search bar, type “Terminal Emulator”.
Step 3: From the search result, tap on Terminal Emulator for Android.
Step 4: Install the app and after installing the app, open it.
Step 5: Once the app opens, type “su” on the terminal window. Tap on Search or Enter.

“su” stands for super-user command line. If the phone is rooted, you will see “$” sign turn into “#” sign in the command line. If the phone is not rooted, you will see a message “command not found”.
See if security features disabled or not
Rooting often compromises built-in security measures. If you notice that your device's encryption has been disabled, or if you’re suddenly able to bypass lock screen protections without your PIN, password, or biometric data, this is a red flag.
Fail to update Android system
Rooted devices often encounter issues when trying to install official system updates. If you’ve received notifications for system updates but they fail to install or keep returning errors, your device could be rooted. Rooting can alter system files, which prevents the update process from completing successfully.
Banking or secure apps Malfunction
Many banking apps, mobile payment services, and security apps are programmed to detect rooted devices for security reasons. If apps like Google Pay, Samsung Pay, or banking apps are suddenly malfunctioning or displaying warnings, your phone may be rooted. These apps rely on the integrity of the operating system and will often refuse to work on rooted devices.
Can You Unroot a Rooted Phone?
Yes, it is possible to unroot a rooted phone, and there are several methods to do so. Unrooting your phone can restore it to its original state, which may be necessary for various reasons, such as regaining warranty coverage or fixing issues caused by rooting. Here’s how you can unroot your phone:
Use a root uninstaller app
Many root management apps like SuperSU or Magisk Manager offer built-in options to unroot your device. Simply open the app, find the unroot option, and follow the instructions. This method usually reverts the changes made during rooting and removes root permissions. Here's how to unroot a device with SuperSU:
Step 1: Go to your app drawer and tap on SuperSU app icon to launch it.

Step 2: Go to the "Settings" tab on the app and look for the option “Full Unroot”.
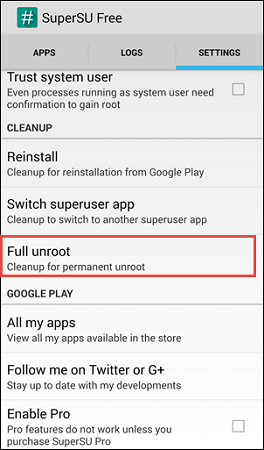
Step 3: Select the "Full Unroot" option.
Step 4: You will get a confirmation message. Tap on Continue button.
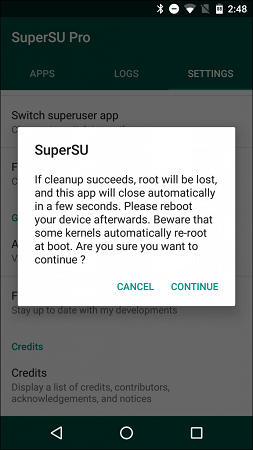
This will unroot your phone, and you will start receiving OS updates and security patches.
Flash the stock firmware
Flashing the original firmware or ROM provided by the manufacturer can effectively unroot your phone. This process involves downloading the official firmware for your device and using tools like Odin for Samsung phones or SP Flash Tool for MediaTek devices. This method will restore the phone to its factory state.
Perform a factory reset
A factory reset can remove root access, but it’s not always a guaranteed solution. It will erase all data and settings on the phone, which might help in removing root-related modifications. However, if the root was achieved through custom recovery or ROM, a factory reset alone may not be sufficient.
Reinstall the operating system
If other methods fail, manually reinstalling the operating system can remove root access. This involves using tools and procedures specific to your device to reinstall the OS from scratch. This method is more complex and typically used as a last resort.
How to Protect a Rooted Android Phone
If you find out that your phone is already rooted or you have rooted it yourself, you should immediately install an anti-spyware app. Rooted devices are easy targets of hackers and scammers due to low-security level of a rooted device. Among all the anti-spyware apps, ClevGuard Anti-Spyware stands above all to effectively protect your Android phone, due to its useful features and their advantages.
Advantages of using ClevGuard Anti-Spyware on rooted phones
Scanning and detection – Spyware presence is very likely in a rooted device. You can scan your device instantly and detect the presence of any spyware.
Instant deletion – After detection, you can delete any malicious file or app instantly. You can resolve other security issues with your phone with a single tap.
Real-time protection – This is the most useful feature on this app, whereby the app will continuously monitor any download on your phone. If the downloaded file or app is malicious in nature, it will alert you to delete it immediately.
App auditing – When you root your device to install third-party apps from external sources, this feature can be your savior. It provides a complete report on any app and outlines the risk involved associated with its app permissions. Additionally, it can find out and remove spyware from Android.
Whitelisting – Lastly, you can whitelist any app or file so that the scanner skips it every time you scan your phone to detect common spyware apps.
How to install ClevGuard Anti-Spyware
Step 1: Click the below button to go to Google Play Store. Install the app from the search result and open the app.
Step 2: You can tap on Scan button on the home screen to scan your phone for spyware presence.
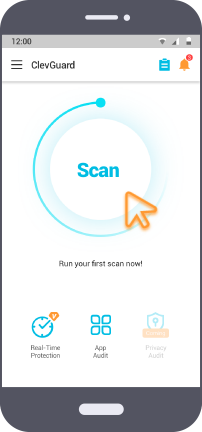
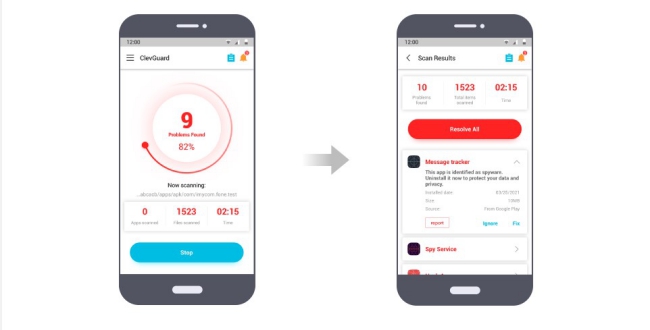
Step 3: After scanning is complete, you can tap on Resolve All button to fix all the issues with your rooted phone.
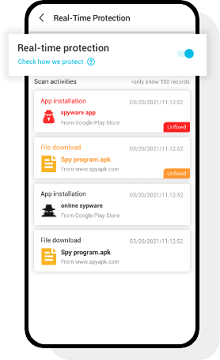
Step 4: You can then go to Real-Time Protection tab at the bottom and toggle it on for 24/7 protection from malware and spyware.
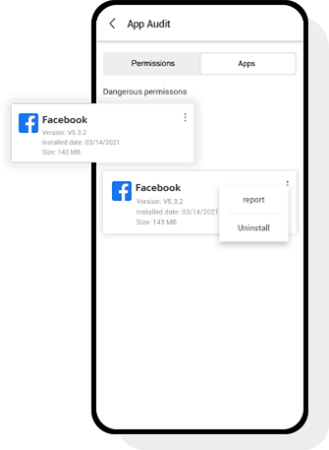
Step 5: You can also go to "App Audit" tab at the bottom to find out the risk level associated with any external app.
Conclusion
Hopefully, we have answered your question on how to check if my phone is rooted. You can check it without an app, but checking with an app like root checker will give you full confirmation. If your phone is rooted, it is very important that you install an anti-spyware app to prevent any malware or spyware attack. We recommend ClevGuard Anti-Spyware for complete real-time protection.
FAQs About Telling If Your Phone Is Rooted
Q1: Can I Check if my phone is rooted without an app?
A: Yes, you can check the app drawer to find SuperSu or Kinguser app installed or not. If any of them is installed, this means your phone is rooted. Similarly, you can go to Settings> About Phone> Status Information> Phone Status. If the phone status is custom, this means your phone is rooted.
Q2: Can my phone be rooted without me knowing?
A: Yes, your phone can be rooted without your knowledge. This might happen if you buy a used phone that’s already rooted, if someone gets access to your phone and roots it, or if you accidentally install a malicious app. To stay safe, only download apps from trusted sources, use strong passwords, and check your phone for any unusual changes with an anti-spyware app like ClevGuard.
Q3: How to check if device is rooted or not in Android programmatically?
A: To check if an Android device is rooted programmatically, you can use several methods: a) check for su binary: look for the su binary in common directories, as it's a sign of root access; b) detect root management apps: check if root management apps like SuperSU or Magisk are installed. c) check system properties: look for system properties or files that indicate root modifications. and d) execute commands: attempt to execute commands that require root access and check for success.








